HearingLife is the Official Hearing Care Partner of USA Pickleball™. Learn more >

Our customers say
4.8 out of 5 based on 52,749 reviews
as of 02/07/2024
Improve your hearing in 3 steps
Hear what our customers are saying
Hearing care you can count on
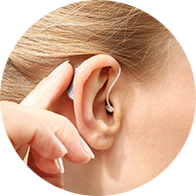
Modern hearing aids for those with hearing loss